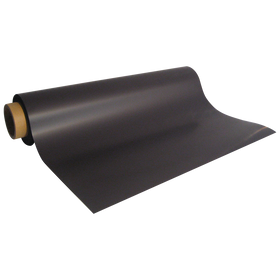
Enamel Copper Winding Wires 100gm (1.02mm) 19SWG
Same Day Dispatch
Order before 1pm to qualify for same day dispatch.
Enamel Copper Winding Wires 100 grams
This 100 gm roll of enamelled copper winding wire is designed for the creation of electro magnets and has a very thin insulating coating, allowing it to be wrapped tightly around an object to create an electro magnet, a motor, a solenoid or any other magnet operated piece of machinery.
Features
- 19 SWG ( gauge)
- Enamelled copper style
- 100 gm roll
- 1.02 mm diameter
- 21.3 ohms per 1000 m
- 13Mtr approximate length
Enameled wire is wire (such as magnet wire) coated with a very thin insulating layer.
It is used in applications such as winding electric motor coils, speakers and transformers.
It is also used in the construction of electromagnets and inductors.
"The core material is copper or aluminum, coated with a thin layer of a polyurethane, polyamide, or polyester etc resin - the so-called "enamel".
Aluminum is lighter than copper, but has higher resistivity" - Wikipedia
Returns Policy
If you are not entirely satisfied with your purchase, we're here to help.
We have a 30 Day Returns policy at Frenergy Magnets. You may return your item within 30 days of receiving it to receive a refund.
The product/s must be unused and in the same condition you received them in. Please contact us at info@frenergy.com.au to initiate the returns process.
The buyer is responsible for the cost of returning the order.